What are Cookies and How to Delete Cookies from your Browser

Many of you would have heard about the term cookies, but how many of you actually know what a cookie is? What it is used for? How many types of cookies are there? How can we delete cookies?.
Cookies are essential to the modern internet experience. They are basically small pieces of data that a server sends to your browser. They make your online experience easier by saving browsing information.
In this article, we will try to answer each and every one of your questions. So without further ado let's get started.
HTTP Cookies and How to Clear Cookies from your Browser
What is an HTTP Cookie?
An HTTP Cookie also called web cookies, Internet cookies, browser cookies, or simply cookies is a small piece of data that a server sends to the user's web browser. The cookies then get stored on the device by the user's web browser. The browser may send it back to the same server with later requests.
Data stored in a cookie is created by the server upon your connection. Whenever you visit a website by typing its address or by clicking on the website link, the server creates a cookie and sends it to the client i.e. the user's browser.
This data is labeled with an ID unique to the user and user's computer, so that later on when the same cookie is sent back with a request to the server, the server can use the unique ID of the cookie to identify the user and can then know which information to serve the user. Also, note that the server can send multiple cookies to the user.
Why do we need Cookie?
So far we know that cookie is a piece of data created and shared by the server to the user's web browser. But why do we need a cookie? What purpose does it serve in the web world? You would be amazed to know how much important a cookie is and how widely it is used.
To understand the role of cookies, first, let me give you a brief overview of how a typical HTTP request works. When you type a web address in the address bar of your browser, the browser then sends the request to the server containing that website, the server then accepts the request and sends a response back to the user browser with the data requested by the user.
Now, there is one more crucial thing in HTTP, and that is, HTTP by itself is a stateless protocol. Stateless here means that each request received by the server is treated as a new request, even if the request is coming from the same user browser. In other words, the server doesn't retain information about each user over multiple requests.
But you may think what does HTTP being stateless has to do with the use of Cookies. To better understand the role of cookies, consider the following scenario (without using cookies), suppose you want to see a movie or show on Netflix, so you go to your computer, open the browser, and type Netflix.com on your web browser, the server sends you the login page and you log in using your credentials and then voila your are in your Netflix account.
Now you select the show you looking for and the browser makes a request to the server to serve the requested show, now, since the HTTP itself is a stateless protocol the server has no way of identifying that you are the same user that just logged in, so the server will then again ask you to verify yourself and then after successful verification, the server will serve the requested show.
Now suppose you now want to watch a movie, so you click on the movies tab, the browser will send the request to the server to fetch the movies, the server will again treat it as a new request and will ask you to verify yourself. How tedious would it be to navigate Netflix, if for each request you would have to verify again, the user experience would not be good.
That's where cookies come in. Cookies contain the data that the server can use to identify you so that you don't have to verify yourself again and again. With cookies, when you login into your Netflix account, the Netflix server creates a cookie with an ID that is unique to you and stores it on your browser.
Each time when you make a request or multiple requests to the Netflix server, the browser sends the request along with the cookie to the server, the server then checks the cookie for validity and then proceeds on fulfilling the users request without having the user authenticate again and again for each new request.
So this was one of the use cases to make you better understand why we need cookies. The key takeaway from the above example is that cookies are a piece of data that helps the server to identify you over multiple HTTP requests.
Hope you got an idea about why we need cookies. Next, we will talk about different types of cookies.
Types of HTTP Cookies
Session Cookies
A session cookie is sent by the server to the user's web browser for temporary use for a limited time frame. The main purpose of the session cookie is to track the user when he is visiting the website. The cookie lets the server know which page components the browser has already sent, so the server doesn't waste time re-sending them.
Session cookies are used where the server needs to track user activity. For example, while visiting an e-commerce website, the session cookie stores the items that the user has added to their cart so as they browse through the site, the items in the cart will follow them.
When the session is ended, meaning users close the website, the session cookies are automatically deleted from the browser.
Persistent Cookies
Persistent cookies are cookies that are used to store user preferences, settings, or sign-on credentials that a user has previously saved. Persistent cookies are permanent cookies and are stored on a user's hard drive until it expires or until the user deletes the cookie.
Persistent Session Cookie expires at a specific date or after a specific length of time. As long as the cookie's lifetime, its information will be transmitted to the server every time the user visits the website that it belongs to, or every time the user views a resource belonging to that website from another website. Persistent cookies track visitors as they move around the website to figure out what people like about the website to help improve the user experience.
Third-Party Cookies
Third-party cookies are those cookies that are created by domains other than the one the user is currently visiting.
These cookies are mainly installed by advertisers that are showing ads on the website the user is currently visiting. They are mainly used for tracking users' activity over the web and for online advertising purposes.
That is why when you click on an advertisement on some page, you see the same advertisement everywhere on the web. There is a term for that and it is called ad retargeting, where a visitor is tracked around the web and shown ads based on the products or services they’ve viewed or interacted with.
How to clear Cookies?
In Chrome:
On your computer, open Chrome.
At the top right, click More.
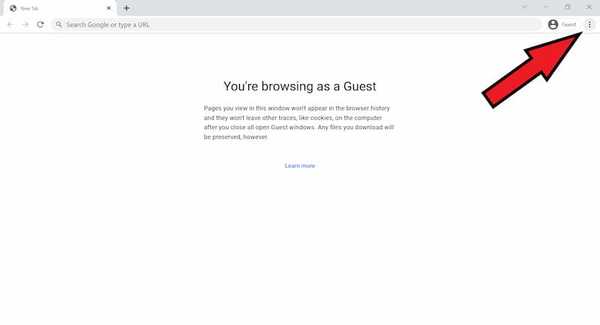
- Click More tools. and then Clear browsing data.
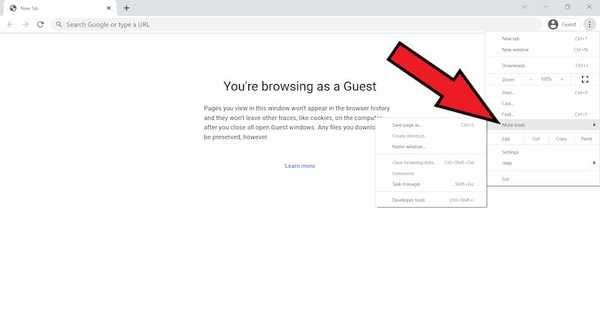
- Next click on clear browsing data.
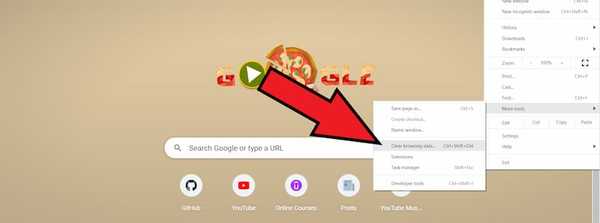
At the top, choose a time range. To delete everything, select All time.
Next to "Cookies and other site data" and "Cached images and files," check the boxes.
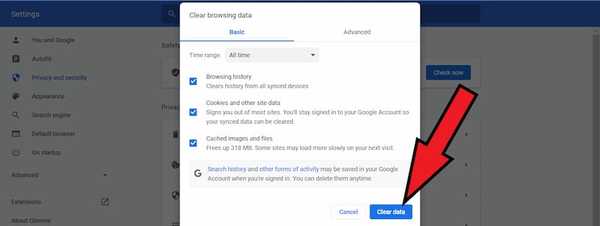
- Click Clear data.
You can also use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Shift+Del to go to the clear data page.
In Brave
On your computer, open Brave.
At the top right, click on the Burger Menu.
- Next Click on settings.
- Next click on Privacy and Security.
- Click on Clear browsing data.
- Next to "Cookies and other site data" and "Cached images and files," check the boxes.
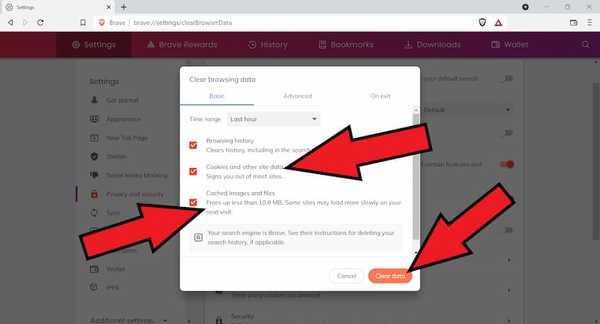
- Click Clear data.
In Edge
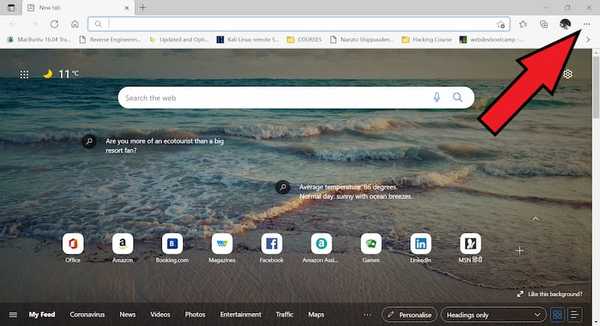
On your computer, open Edge.
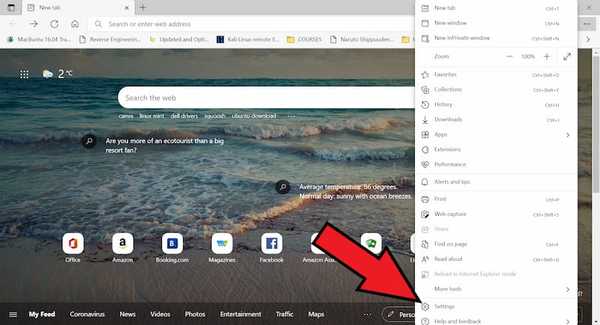
At the top right, click on three horizontal dots next to your profile picture.
- Next Click on settings.
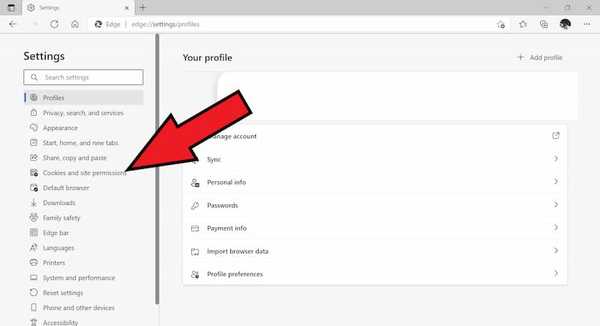
- Next click on Cookies and site permissions.
- Click on Manage cookies and site data.
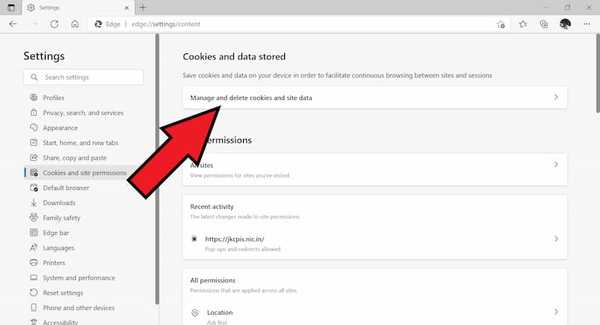
- Next click on see all cookies and site data.
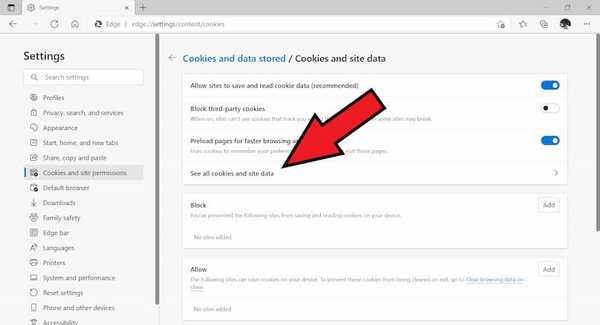
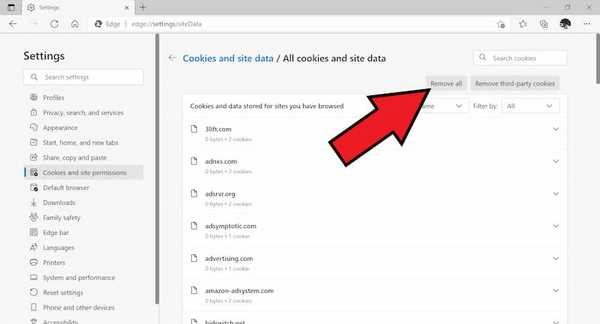
- Now Click on remove all.
In Firefox
On your computer, open Edge.
At the top right, click on the Burger Menu.
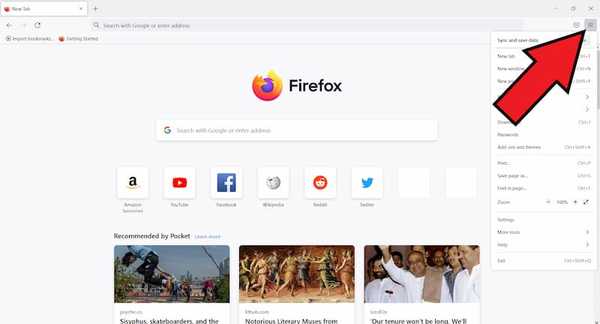
- Next Click on settings.

- Next click on Privacy and Security.
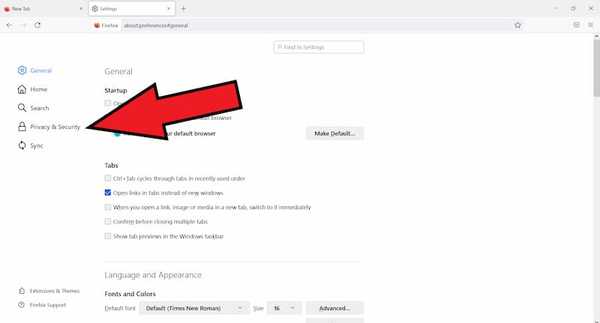
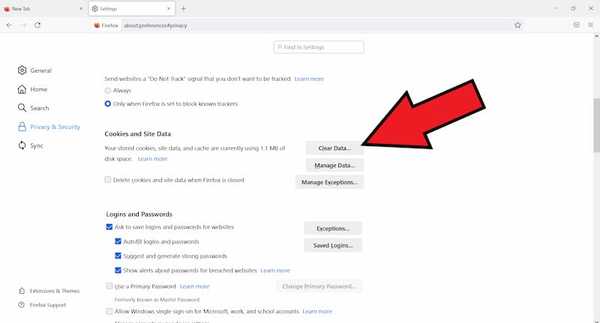
- Scroll down to cookies and site data and click on clear data.
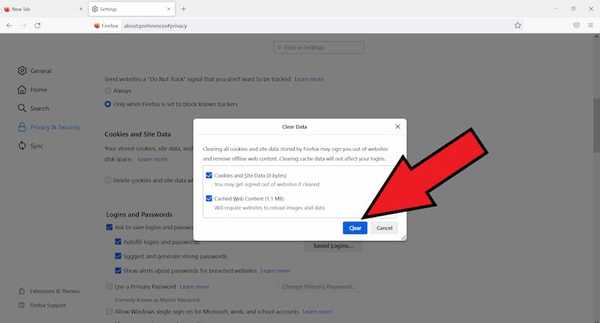
- Next click on clear button on the clear data popup.
Final Words: HTTP Cookies and How to delete them
Although, cookies are useful and without them, the overall user experience of browsing the web would deteriorate, but they have some privacy concerns. Advertising companies can track a user across all pages where it has placed advertising images and can then use that knowledge to target advertisements to the user's presumed preferences.
Also, you can't just turn cookies off permanently as it would make navigation on certain websites difficult. However, by clearing tracking cookies and super cookies, you can prevent the invasion of your privacy online.
I hope you got a better idea of what cookies are, what role they play, and how you can clear them, and if you liked the article, consider following us on Twitter to get the latest tech news and updates.
